1.0 CORPORATE GOVERNANCE IN BBK:
Corporate governance is the framework by which business corporations are directed and controlled. It describes a set of relationships between a company’s management, its board, its shareholders and other stakeholders that provides the structure through which the objectives of the companies are set, and the means of attaining those objectives and monitoring performance are determined. The corporate governance structure specifies the distribution of rights and responsibilities among different participants such as the Board, Management, shareholders and other stakeholders, and spells out the rules and procedures for making decisions on corporate affairs. It influences how the objectives of the Bank are set and achieved, how risk is monitored and assessed, and how performance is optimized. The corporate governance structure of BBK is designed to enshrine the concepts of good governance as required by the Corporate Governance Code of the Kingdom of Bahrain issued by the Ministry of Industry and Commerce, the Central Bank of Bahrain (CBB) in their High-Level Controls (HC) Module, Basel II paper on ‘Enhancing Corporate Governance’ of 2006, Bahrain Commercial Company Law and other supporting references.
The guidelines provided herein are to support the principles stated in any other of the Bank’s prevailing governance documents and related policies. The Bank (BBK Group) also adheres to the Code of Best Practice on Consumer Credit and Charging (prepared jointly by the Bahrain Association of Banks and Central Bank of Bahrain).
Bank’s Wholly owned subsidiaries have their own Boards of Directors with separate Board charters. However, as a Group these subsidiaries shall abide by the corporate governance principles set out in this framework. For strategic decisions these subsidiaries will refer to the mother company’s Board of Directors with recommendations.
2.0 BBK’S CORPORATE GOVERNANCE PHILOSOPHY:
High standards in corporate governance are fundamental in maintaining BBK’s leading position within the local and regional banking sector and the community. Continuous review and adherence to strong corporate governance practices help enhance compliance levels according to international standards and best practice.
BBK shall continue its endeavor to enhance shareholders value, protect their interests and defend their rights by practicing pursuit of excellence in corporate life. The Bank shall not only comply with all statutory requirements but also formulate and adhere to strong Corporate Governance practices.
BBK shall continuously strive to best serve the interests of its stakeholders including shareholders, customers, staff and public at large with particular emphasis on Environment and Social Governance (ESG) and sustainability reporting, which takes into consideration the UN Sustainable Development Goals into consideration.
The adoption and implementation of Corporate Governance would be the direct responsibility of the Board of Directors, in line with the regulatory and statutory requirements in the Kingdom of Bahrain and other countries where BBK operates. Corporate Governance disclosures shall be made according to the CBB’s requirements as per its rulebook modules PD 1.3.8 and PD 6.1.1 and amendments thereto.
3.0 CORPORATE GOVERNANCE MODEL:
The standard Corporate Governance model interconnects the dynamic relation between the three main stakeholders namely Shareholders, the Board and the Management. The roles of shareholders, the Board and the Management are distinctly different but complimentary to the core objectives and functioning of the institution. Such model can be drawn as under. BBK’s CG model is based on Angelo-American model expanded to include a variety of stakeholders who have interest in the Bank and its success.
BBK’s Corporate Governance practices ensure a healthy relationship with all the stake holders while achieving core objectives of the institution.
3.1 Board of Directors:
The Bank’s Board of Directors is accountable to the Bank’s shareholders and other stakeholders, to ensure that the Bank is managed in a safe and sound manner. To fulfill their fiduciary duties, the Directors must be independent of the Management of the Bank; familiar with the Bank’s business and general financial and accounting principles; and actively engaged in directing and overseeing Management.
3.2 Management Team:
The Bank’s Executive Management team is accountable to the Board to manage the Bank in accordance with the policies and principles established by the Board and applicable legal and regulatory requirements.
3.3 Subsidiaries and Overseas Branches:
Bank will ensure that, as a minimum, the same or equivalent corporate governance requirements would apply to its overseas branches and to subsidiaries. The Corporate Governance framework for BBK covers all subsidiaries and overseas branches. Subsidiaries would also adopt their own corporate governance policies and frameworks being independent licensees. Some requirements, however, would be met by subsidiaries through BBK’s corporate governance status. Some of the functions of the subsidiaries such as audit, nomination & remuneration can be outsourced to the main Bank, if recommended by their Boards. The subsidiaries would periodically and on need based basis report to the Bank’s Board.
4.0 PURPOSE OF THIS FRAMEWORK:
The purpose of this Framework is to outline the corporate governance structure for the Bank.
This Corporate Governance Framework document together with the Board Charter and the terms of reference of all Board Committees, Code of Conduct for Directors, Directors Remuneration and Compensation Policy, Key Persons Dealing Policy, Disclosures Policy and such other independent policies related to Corporate Governance will form the Corporate Governance Policy Manual and would be the reference document for the Board and the Management.
The individual policies/documents may change with market and regulatory requirements from time to time and will be suitably replaced
5.0 CORPORATE GOVERNANCE PRINCIPLES:
TThe Bank will follow the corporate governance principles as issued by the Ministry of Industry and Commerce in the Corporate Governance Code and the CBB as per the High-Level Controls (HC) Module of the Rulebook. The principles are as follows:
- The Bank shall be headed by an effective, collegial and informed Board.
- The approved persons must have full loyalty to the Bank.
- The Board must have rigorous controls for financial audit and reporting, internal control, and compliance with law.
- The Bank must have rigorous and transparent procedures for appointment, training and evaluation of the Board.
- The Bank must remunerate approved persons fairly and responsibly.
- The Board must establish a clear and efficient management structure.
- The Bank must communicate with shareholders, encourage their participation, and respect their rights.
- The Bank must disclose its corporate governance.
Building on the above, the Bank’s guiding principles of good corporate governance are:
5.1 CORPORATE GOVERNANCE PRINCIPLES:
5.1.1 The Board would consist of Directors representing varied/appropriate mix of applicable skills and experience and meeting ‘fit and proper’ requirements of the CBB.
5.1.2 There will be separation and clear division in the roles and responsibilities of the Chairman and the Chief Executive. The Chairman of the Board will be an Independent Director.
5.1.3 Bank would have a nomination process designed to ensure that the appropriate balance and capability of the Board is maintained on the basis of periodic evaluation of the performance of the Board, its Committees and individual Directors.
5.1.4 Bank will have a fair representation on the Board by Directors, including adequate ‘independent’ Directors, to meet minimum regulatory requirements and to facilitate objectivity in decision making.
5.1.5 Bank will provide the Directors with access to training (particularly on induction) and professional advice on issues when required.
5.2 Strategy – the Board’s role in the strategy development process will ensure:
5.2.1 Active Board participation in strategy development, including the review and challenge of the strategy.
5.2.2 Creation of an adaptable organization that is able to respond quickly to changing market opportunities.
5.2.3 Appropriate dissemination of the strategic plan of Bank.
5.3 Corporate Culture - the Board’s role in setting and communicating standards for organisational behavior shall:
5.3.1 Promote openness with Management on issues for which the Board will ultimately be accountable.
5.3.2 Sponsor and actively promote adherence to the organization’s defined code of conduct.
5.3.3 Promote the use of incentive schemes that align the interests of the Board and Executive Management with those of the shareholders and other stakeholders.
5.4 Monitoring and evaluation – the Board’s role in monitoring Management and evaluating its performance against defined goals will require to:
5.4.1 Ensure that the organization complies with relevant laws and regulations as well as with accounting, human resource and other internal policies.
5.4.2 Understand organizational risks and be informed routinely about how they are managed and be assured that this is effective.
5.4.3 Apply a rigorous process for evaluating and monitoring the performance of the Chief Executive (“CE”) and Executive Management.
5.5 Stewardship – the Board’s responsibility towards stakeholders and accountability for their interests will need to:
5.4.1 Ensure that the organization complies with relevant laws and regulations as well as with accounting, human resource and other internal policies.
5.4.2 Understand organizational risks and be informed routinely about how they are managed and be assured that this is effective.
5.4.3 Apply a rigorous process for evaluating and monitoring the performance of the Chief Executive (“CE”) and Executive Management.
5.6 Risk Management
The Board is responsible for ensuring that the Bank has a robust Risk Management Framework. The Bank has in place a comprehensive Risk Management Strategy, a strong Risk Appetite Framework (see Appendix A) and a detailed Policy Manual which are approved by the Board. These provide an environment of strong risk & credit governance and a robust credit management framework.
6.0 CORPORATE GOVERNANCE STRUCTURE:
The Board is responsible for ensuring that the Bank has a robust Risk Management Framework. The Bank has in place a comprehensive Risk Management Strategy, a strong Risk Appetite Framework (see Appendix A) and a detailed Policy Manual which are approved by the Board. These provide an environment of strong risk & credit governance and a robust credit management framework.
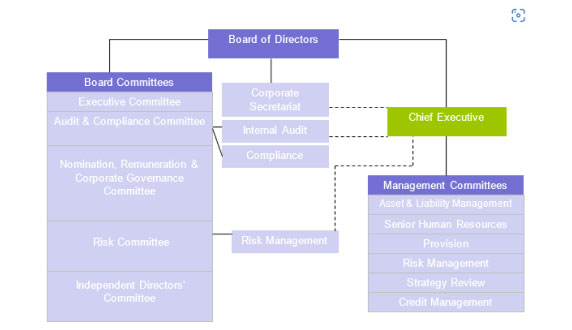
The role of the Group Corporate Secretary is to assist the Board and its Committees in maintenance of relation between Executive Management and the Board, and between the Board and shareholders and vice versa. The financial control function would be independent of the business lines. The Audit function would be independent and report to the Audit Committee of the Board. The Risk Management would be independent and report to the Risk Committee of the Board.
6.1 Board Committees:
The Board delegates (without abdicating) some of its responsibilities to different Board Committees. The present established Board Committees are given below. The terms of references have been separately established for each Committee.
Executive Committee
- Minimum five members are appointed for a 1 year term.
- Minimum number of meetings required each year: 8
- Role: reviews, approves/recommends and directs the Executive Management on matters raised to the Board of Directors
Audit Committee
- Minimum three members are appointed for 1 year term.
- Minimum number of meetings required each year: 4
- Role: reviews the internal audit programme and internal control systems, considers the major findings of internal audit review, investigations and Management’s response and ensures coordination between internal and external auditors Tracks, monitors and reports trading activities of Key Persons and Insiders in accordance with the requirements of CBB and the Bahrain Bourse Company.
- Nomination, Remuneration and Corporate Governance Committee
- Minimum three members are appointed for a 1 year term.
- Minimum number of meetings required each year: 2
- Role: establishes a Board compensation policy for the Directors and Executive Management, recommending Board members’ appointments to various Committees, to the Board for approval, in addition to reviewing, assessing and having oversight on all aspects of Corporate Governance in keeping with the regulatory and statutory requirements.
Risk Committee
- Minimum four members are appointed for a 1 year term.
- Minimum number of meetings required each year: 4
- Role: establishes an effective risk management framework through appropriate risk policies/processes, monitors risk profile of the Bank to ensure that it is in accordance with risk appetite of the Bank.
Independent Directors’ Committee
- Comprises of Independent Directors only
- Minimum number of meetings required each year: 1
- Role: provide independent analysis of issues raised to the Board and raise recommendations to the Board if required including determining whether decisions taken by the Board or its other Committee have any material of negative impact to the interests of the minority/small shareholders of the Bank
The Board reserves the right to form temporary Committees and discontinue them, from time to time as it sees it necessary.
6.2 Management Committees:
Management Committees are chaired by the Chief Executive and, other Committee members are heads of the relevant divisions appointed by the Committee Chairman. Specific terms of references have been established for each Committee formed.
The Group Chief Executive reserves the right to form temporary Committees and discontinue them, from time to time and as necessary. Some of the main Management Committees are:
- Committee
- Summery Terms of Reference
- Asset & Liability Management
- Establishes strategies and guidelines for the overall management of the balance sheet and its associated risks.
- Senior Human Resources
- Establishes appropriate policies, procedures and guidelines for the management of human resources.
- Provision
- Reviews and establishes provisioning requirements for loans, advances and investments.
- Risk Management
- Identifies, measures, monitors and controls risk by establishing risk policies and procedures.
- Strategy Review
- Reviews and monitors progress on strategic initiatives.
- Credit Management
6.3 Delegation of authority
The Board Committees, Management Committees and other specific Management personnel will execute activities/transactions on behalf of the Bank in accordance with the delegated authority limits. As a principle, policies covering operational issues, internal control, risk management, human resources, IT, compliance and such other functions in the Bank would be approved by the Board. The approval of relative Procedure is delegated to the Chief Executive.
The procedures / processes relating to the functioning of the Board or Board Directors would be would be part of the Board Charter or approved either by the Board or by the appropriate Board Committee.
The application of the authority limits to different functionaries will be based on principles of delegation and will form part of the relevant Policy and Procedure.
Appendix A
Risk appetite statement:
Risk appetite is the level and type of risk that the Bank is willing to assume in order to achieve its strategic and business objectives, keeping in perspective the obligations to its stakeholders.
The risk appetite of the Bank is both a qualitative and quantitative measure, and reflects its level of risk tolerance in normal as well as in stressed scenarios. It is expressed as a measurable key performance indicator (KPI), a tolerance limit, or as a qualitative guideline.
The Bank has a well-defined Risk Appetite Framework, that consists of the Risk Appetite Statement along with: (a) well-defined performance metrics in the form of Key Performance Indicators or KPIs; (b) risk limits, exposure criteria, restrictions and controls, lending and investment standards as laid out in the internal risk policies and procedures manual; (c) capital and liquidity benchmarks, which are monitored in the Asset Liability Management Committee meetings; (d) key business and risk management objectives, goals and strategy, which are defined in business, investment and risk management strategies; and (e) management and oversight structures in the Bank through Management and Board committees. Our risk appetite defines the desired performance levels, which, in turn, are embedded into management of the various risks within the Bank as well as the capital of the Bank. Our risk appetite is integrated into the strategic, capital, and risk management planning process across business verticals. The Bank measures the contribution of each business vertical towards key KPIs.
The Bank aims to optimise the risk-reward for the benefit of all stakeholders, and this is reviewed and implemented through strategies (business, investment, risk management, ICAAP), which are closely reviewed annually. The Bank’s primary exposure is to credit risk along with other Pillar 1 and Pillar 2 risks assumed in the normal course of its business. The risk appetite statement is also reviewed though a Risk Management Strategy document by management, and recommended for approval to the Risk Committee and the Board annually. The Bank’s risk appetite requires, amongst other things:
- A high level of integrity, ethical standards, respect and professionalism in our dealings.
- Taking only those risks which are transparent and understood, and those which can be measured, monitored, and managed.
- Ensuring that the Bank has adequate levels of capital adequacy on an ongoing basis as mandated by the regulator (currently 12.5 percent), and as assessed by the Bank in its ICAAP document; that the capital requirements and capital planning are incorporated in its capital management strategy.
- Ensuring that the Bank has access to adequate levels of stable, efficient, and cost-effective funding to support liquidity and lending or investing requirements on an ongoing basis; that the Bank has in place a robust liquidity management framework and contingency plans to monitor and manage liquidity both in normal and stress liquidity conditions, in addition to monitoring key liquidity ratios (internal and regulatory) in Asset Liability Management Committee meetings on a monthly basis.
- Adhering to the core principles of lending, which are enshrined in the general lending policy of the Bank.
- Maintaining a robust credit management framework with focus on geographies where the Bank has physical presence (Kuwait, India, Dubai), GCC, and select MENA and other countries; undertaking exposures to countries within the directives of the Country Risk Committee, which reviews country risk and the Bank’s strategy in those countries on a dynamic basis.
- Having in place a defined monitoring, collection and restructuring framework for effective recovery mechanism.
- Limiting exposures to high-risk activities which may culminate in tail-end risks, jeopardising the Bank’s capital and creditworthiness.
- Striving for optimum profitability through income generation, cost efficiency, and low impairment.
- Widening the product basket and delivery channels for increasing customer satisfaction; assessing new credit products in a structured form for approval by appropriate authorities, so that the underlying risks, benefits, operational processes, system/technology requirements, and legal requirements are understood and managed.
- Protecting the Bank’s and the customers’ interests through robust operational procedures, internal controls, system support, training and operational risk management processes to mitigate operational risk.
- Ensuring full compliance with legal, statutory, and regulatory requirements; ensuring adherence to anti-money laundering (AML) and other obligations under international law; providing adequate training and guidance to mitigate compliance and AML risks.
- Approves credit and investment proposals of a certain limit. Also reviews and recommends any proposals requiring Executive Committee or Board approvals.
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience and by clicking “I Accept” below, you consent to the use of cookies. Learn more



